BOFIT Weekly Review 30/2020
Manufacturing and fixed investment sustained China’s economic growth in the second quarter
The National Bureau of Statistics reports a rapid recovery of the Chinese economy in the second quarter. After a real GDP contraction of 6.8 % in the first quarter, GDP grew by 3.2 % y-o-y. The recovery is expected to continue for the rest of this year. Most forecasts see 2020 GDP growth coming in at around 1–2 % (BOFIT Weekly 26/2020).
The Chinese recovery is best described as mixed. China seems to have again turned to debt-fuelled fixed investment to stimulate growth. As a result, industrial output and construction have picked up rapidly in recent months, along with an acceleration of indebtedness. In contrast, growth is restrained by declined real disposable household income, weak consumer demand and reduced activity in the services sector from last year. The structure of China’s economy has in recent years shifted slowly from one dominated by industrial activity and fixed investment towards a model led by services and consumption. This development is now backtracking significantly.
Fixed investment was the big driver of GDP growth in the second quarter
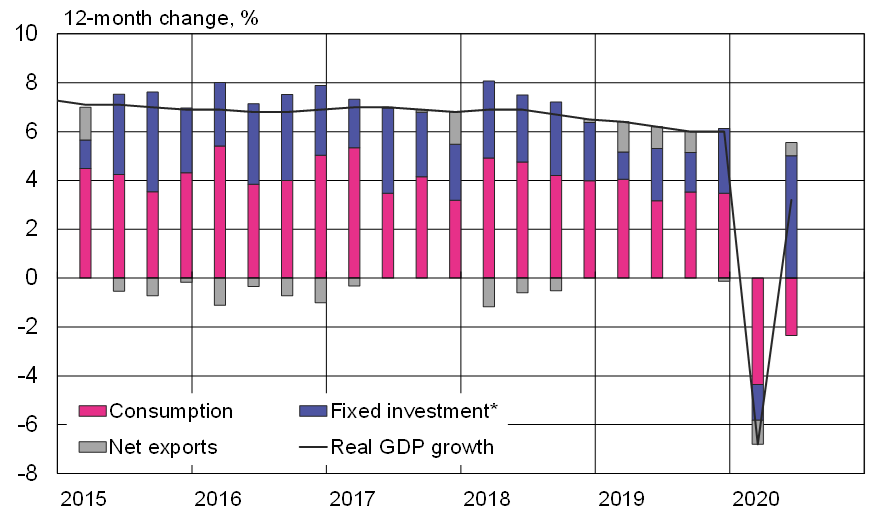
*) Includes changes in inventories.
Sources: China National Bureau of Statistics, CEIC and BOFIT.