BOFIT Weekly Review 34/2020
China’s economic recovery stabilising
The Chinese economy has so far staged a remarkably robust recovery since hitting bottom in January-February. However, the impacts of the coronavirus and extent of recovery vary considerably across sectors. The National Bureau of Statistics reports that the overall pace of recovery has slowed in recent months in industry, retail sales and fixed investment.
On-year industrial output growth figures have hovered around 5 % in recent months. Notably, manufacturing has bounced back nicely. The manufacture of computers, smartphones, cars and a wide range of home appliances has soared in recent months. This reflects changes in demand brought on by the covid-19 pandemic as people switch to working remotely from home, spend on home appliances and prefer private vehicles to public transport.
Domestic consumer demand continues to contract. In recent months, retail sales have been down by about 3 % y-o-y in real terms. Unemployment is also still above normal and household disposable incomes have shrunk. In some branches, measures to deal with covid-19 still restrain consumption. For example, the reopening of movie theatres began only in late July.
Growth in fixed investment appears to be moderating, but these figures come with huge uncertainty. Growth this year has been largely driven by investment in infrastructure and real estate, while investment in productive capital assets at factories has decreased.
The recoveries in industrial output and retail sales slowed in recent months with growth remaining below pre-corona levels
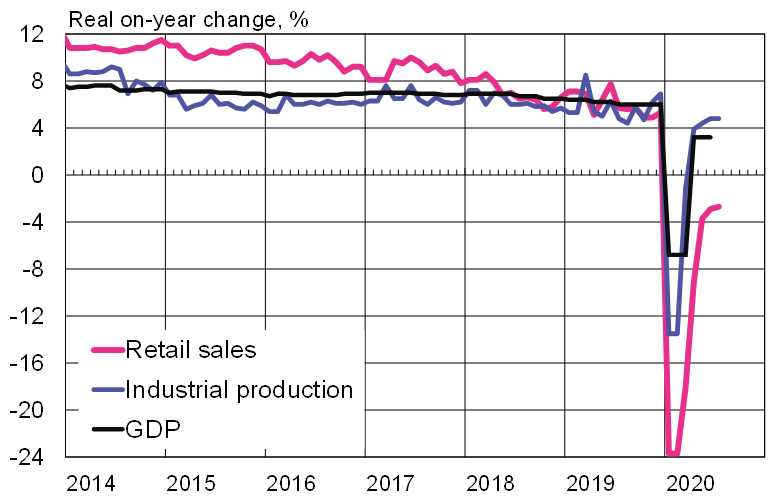
Sources: China National Bureau of Statistics, CEIC and BOFIT.