BOFIT Weekly Review 46/2024
BOFIT expects China's economic growth to keep slowing
BOFIT released its latest forecast for the Chinese economy for 2024–2026 on November 4. With China’s era of high growth fading, the country is gradually shifting to more conventional growth rates. We expect GDP growth to hover around 4 percent this year, slowing to around 3½ percent next year and roughly 3 percent in 2026, a level China should be able to sustain over the longer term.
The most important cyclical factors behind China's economic growth slowdown are weak domestic consumer demand, the ongoing collapse of the real estate sector, and the financial problems facing local governments. Structural factors restraining growth over the longer term include the shrinking working-age cohort, the rising median age of the population, sluggish progress in transitioning from a growth model dominated by fixed investment to a consumption-driven economy, inefficient use of resources, opaque economic policies, and muted productivity gains. Sector-specific differences remain large, with some parts of the economy experiencing high growth and others contracting. Nevertheless, as the world’s largest upper-middle-income country, China’s 3-percent economic growth is quite respectable and on par with the pace of global economic growth.
Our latest forecast for the Chinese economy comes with high uncertainty. While the understated weakness of China’s financial sector constitutes a risk to the country’s economic development, the growth outlook improves dramatically if China makes strong progress in economic reforms. On the other hand, vigorous fiscal stimulus in itself only supports short-term growth, implying later adjustment costs that subdue growth later.
In addition to the customary forecast presentation in conjunction with our China briefing (in Finnish) last week, we discussed the regional economic situation in China, changes in value chains of foreign trade, and China’s future business environment.
China’s GDP growth, factors contributing to growth, and BOFIT forecast for 2024–2026
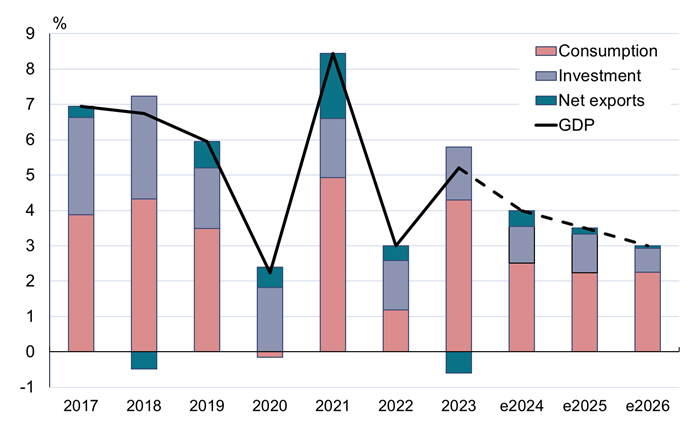
e=estimate
Sources: China National Bureau of Statistics, CEIC, and BOFIT.