BOFIT Weekly Review 02/2022
Despite intense suppression strategy, covid infections in China on the rise
Although the numbers of confirmed covid-19 cases in China are still miniscule (150–250 cases a day), the country has resorted to strict local suppression measures to deal with new fast-spreading strains of the virus. At the end of December, officials put 13 million people in city of Xian in home quarantine. The stay-at-home strategy worked with the rate of new infections in the province falling below ten a day. However, infection rates have climbed in recent days in other regions (e.g. Henan province, Tianjin municipality bordering Beijing and Guangdong province), causing them to impose harsher covid restrictions. Current measures to combat covid have hurt both local economies and global production chains (e.g. the Micron and Samsung microchip foundries in Xian were forced to reduce production). Even so, current measures are estimated to have relatively modest impact on the economy at the national level as they are short in duration and geographically limited.
Vaccination programmes rolled out quickly last year in China. Health officials report that as of Saturday (Jan. 8) 1.2 billion Chinese (about 86 % of the population) had received two doses of vaccine. China has yet to approve any vaccines developed abroad. The most-used domestic vaccines are those developed by Sinovac and Sinopharm. Pfizer-Biontech, whose mRNA vaccine is still awaiting approval by the Chinese authorities, made already last summer an agreement with the Shanghai-based Fosun Pharmaceutical on a joint venture to manufacture vaccines in China.
China’s vaccine exports soared last year. Prior to the covid pandemic, the value of exported vaccines intended for human immunisation averaged just $10 million a month. In the third quarter of 2021, the value of vaccine exports averaged $2.2 billion a month. In October and November, the value of monthly exports fell to $1.4 billion. In terms of vaccine doses shipped, China has exported the most of any country. In addition to its own vaccines, China manufactures vaccines or components for export under licence.
The Sinovac and Sinopharm vaccines are the most-used Chinese vaccines outside China. Both have received use approvals in over 50 countries, mainly emerging and low-income economies. Certain countries have also agreed on local manufacture of Chinese vaccines. Beijing-based Bridge Consulting tracks Chinese vaccine uptake globally. China has sold a total of 1.65 billion doses to foreign customers. China has also committed to donating 150 million doses to other countries. About 60 % of sold and donated vaccine doses have gone to countries in Asia. The countries purchasing the most Chinese vaccines are Indonesia (259 million doses), Pakistan (132 million), Iran (110 million), Turkey (100 million) and Brazil (100 million). The largest recipients of donated vaccines are in Southeast Asia. China has sold 136 million doses to African nations and committed to donate 37 million doses. Some countries like Brazil, Thailand, Malaysia that have bought Chinese vaccines announced that they are discontinuing their use due to the poor levels of protection against new covid variants such as delta and omicron.
Covid case numbers in China have increased in recent weeks
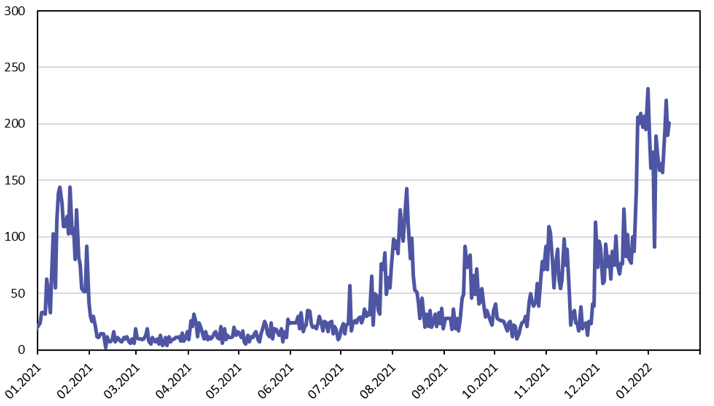
Sources: National Health Commission of China, CEIC and BOFIT.