BOFIT Weekly Review 07/2020
Effects of the coronavirus on the Russian economy remain limited for now
As there is still large uncertainty on the duration and extent of the coronavirus epidemic, the potential impact on the Russian economy is difficult to evaluate. Current information suggests the overall economic impact will remain low. However, if the epidemic widens, it poses significant risks to Russia’s economic development amidst deteriorating global economic conditions.
Russia has experienced two confirmed coronavirus cases. Both are Chinese nationals. Both made full recoveries and have been released from hospital. Measures to prevent the spread of the coronavirus in Russia include restricting passenger traffic at China-Russia border crossings, limiting flights between Russia and China, and suspending visa-free travel for Chinese tourist groups.
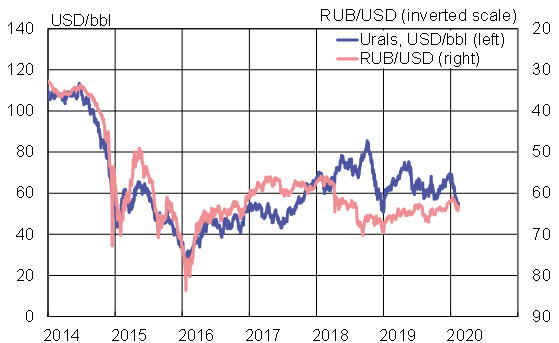
While the coronavirus has caused uncertainty on international markets in recent weeks, the reaction on Russian markets has been subdued. The ruble has lost about 4 % of its value against the dollar and the RTS stock index is down about 1 % from the start of the year.
Commodity markets, however, have seen the price of Ural-grade crude plummet by 20 % since the start of the year. Prices of many metals have fallen as well. The value of Russian exports of oil, natural gas and metals accounted for approximately 17 % of GDP last year. On the basis of the latest oil futures, the average price of oil should reach about 55 dollars a barrel this year. Russia’s 2020 budget is set to show a slight deficit with Urals oil price of 42 dollars a barrel in accordance with the government’s fiscal rule.
Russia’s tourism sector is already feeling the effects of the virus with a drop in Chinese tourists. The Chinese are among the top tourist groups in Russia. Russia’s Association of tourism industry says the industry could lose 40–50 million dollars a month if Chinese group tours scheduled for February and March continue to cancel. Russia's total tourism earnings amounted to 11 billion dollars last year (0.6 % of GDP). In addition to the tourism industry, the epidemic has complicated component deliveries to Russian car factories, as well as disrupted retail chain supplies of fruits and vegetables imported from China.
This year started with falling oil prices and ruble depreciation
Source: Reuters.