BOFIT Weekly Review 36/2017
Changes in area and country structure of Russian goods imports show some stabilisation
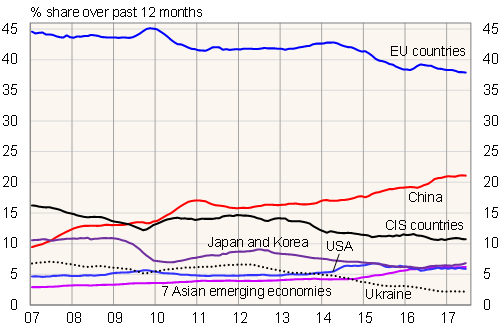
Russian customs figures show that the share of imports from EU countries inched down to 38 % in the first half of this year, a slight drop from 1H15 and 1H16. The share of imports from China and other emerging economies in southern and south-eastern Asia rose to more than 26 %, with China accounting for about 20 % of imports to Russia and these emerging economies exceeding 6 %, largely on growth in imports from Vietnam, Indonesia and India. South Korea's and Japan's share rose to 7 % as South Korea's share of imports increased. The US remained almost unchanged with less than 6 % of imports. CIS countries held on to an 11 % stake as e.g. the decline in Ukraine's share eased. The relative shares shown in Russian import figures should be taken with a recall that the corresponding export figures of trading partners give a partly different picture. For example, the export figures compiled by international agencies suggest that the share of EU countries is clearly larger in Russian imports than indicated by Russia's import figures.
The country structure of Russian imports has seen tangible changes in recent years. The decline of the share of EU countries in imports to Russia in 2014–16 mainly came from the machinery, equipment & transport vehicle category. The same applies to the shares of Japan and South Korea. At the same time, most of the growth in the shares of China and other Asian emerging economies in Russia's imports was due to the machinery, equipment & vehicle category. This category, which includes both investment goods and consumer durables, has been affected, besides the sharp drop in the ruble's exchange rate, by a strong fall in fixed investment and consumption with their accompanying structural changes in Russia, globalisation of production chains for finished products and factors affecting the competitiveness of suppliers.
The rest of the tapering off of the EU countries' share in Russia's imports mainly reflects the impact of Russian countersanctions that were imposed in 2014. The restrictions focus on imports of agricultural products and foodstuffs. The restrictions for their part have helped Asia's emerging economies and China increase their market shares and have also propelled a notable increase in Belarus' share of Russia's imports.
Share of select country groups and countries in Russian imports in 2007–17
Source: Russian customs.