BOFIT Weekly Review 42/2015
Small changes in regional structure of China’s foreign trade
Foreign trade contracted again in September. For the first nine months of 2015, the value of goods exports declined 2 % y-o-y, while the value of imports declined 15 %, mainly on falling prices for energy and commodities. The January-September trade surplus was over $420 billion.
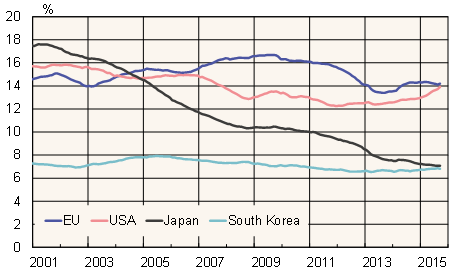
The US and EU remain China’s largest export markets, accounting for 18 % and 15 %, respectively, of total exports. Japan, which accounts for 6 % of Chinese exports, has seen its share fall steadily for years. South Korea, with a 4 % export share, is also an important export market for China. About half of China’s exports go to Asia, while some 6 % goes to Latin America and 5 % to Africa.
Some 13 % of Chinese goods imports come from the EU, followed by South Korea (10 %), Japan (9 %), the US (9 %) and Taiwan (8 %). South Korea and the United States have increased their shares in recent years, while the shares of Japan and Taiwan in China’s imports have declined. Asian countries provided 57 % of China’s imports, while 6 % came from Latin America and 4 % from Africa.
Foreign trade shares of China’s largest trading partners
Source: Macrobond.